
EXPERIMENT
Laser engraving 3D prints
Exploring the laser application of designs onto various filament types
Using a laser engraver to apply a design to 3D printed pieces can be a good way to improve them aesthetically or even improve their functionality. But the process may not be as straightforward as one would expect it to be. The type of laser used, the type of material, and the color of the material can all significantly affect what the final result would be.
Setup
We started out by printing a series of plates in various colors of both PLA and ABS. We printed them face-down on a textured plate, with at least 6 solid layers on the side we planned on trying to engrave; so 6 solid layers or the bottom shell. This will prevent the lasers from burning completely through when they etch into the material.
For this test, we used an xTool F1. It has both a 2 watt infrared laser and a 10 watt blue diode laser. It has a dual-galvanometer configuration, so despite its fairly limited working area of 115mm square, it can accommodate much taller items without any additional accessories or modifications. This makes engraving three-dimensional items much easier.
We used xTool Creative Space, xTool’s proprietary control software. But a similar test file can be set up using Lightburn or other laser cutter control software.
We set up a test file containing text at two different sizes and some simple graphics. For the 2 watt IR laser, we set some 12 point text to outline score at power 90 and 60 mm per second; and also to engrave at power 100 at 200 mm per second and 240 lines per centimeter. Because the IR laser is relatively low power, we set both for 4 passes.
For the smaller 6 point text, we adjusted the settings to power 80 for the scored text, and power 90 and 200 lines per centimeter for the engraved text. Both of those were set to 2 passes.
The simple line graphics using the IR were set at power 100; 60mm per second; and 1 pass.
For the 10 watt Blue Diode laser, all the setup was essentially the same except all the text was set for just a single pass.
Results
PLA: white
2W Infrared laser:
No effect.
10W Blue Diode laser:
No effect.
PLA: grey
2W Infrared laser:
Uneven ‘scarring’ relief. Lighter color than the material.
10W Blue Diode laser:
Uneven melting of the material. Pushed upward and outward of the design.
PLA: black
2W Infrared laser:
Scoring function etched fairly sharply into material. Engraving function a fairly sharp and lighter colored (light brown) relief.
10W Blue Diode laser:
Etched cleanly into the surface of the plate
PLA: red
2W Infrared laser:
No effect.
10W Blue Diode laser:
Etched cleanly into the surface of the plate
PLA: brown
2W Infrared laser:
Sharp, lighter colored (light grey) relief.
10W Blue Diode laser:
Etched into the surface of the plate, some uneven melting.
ABS: white
2W Infrared laser:
Sharp black lines. No relief.
10W Blue Diode laser:
No effect.
ABS: black
2W Infrared laser:
Produced sharp and lighter colored (light brown) relief.
10W Blue Diode laser:
Etched sharply and cleanly into the surface of the plate.
ABS: yellow
2W Infrared laser:
Sharp black lines. No relief.
10W Blue Diode laser:
Etched into the surface of the plate, minor uneven melting.
Samples
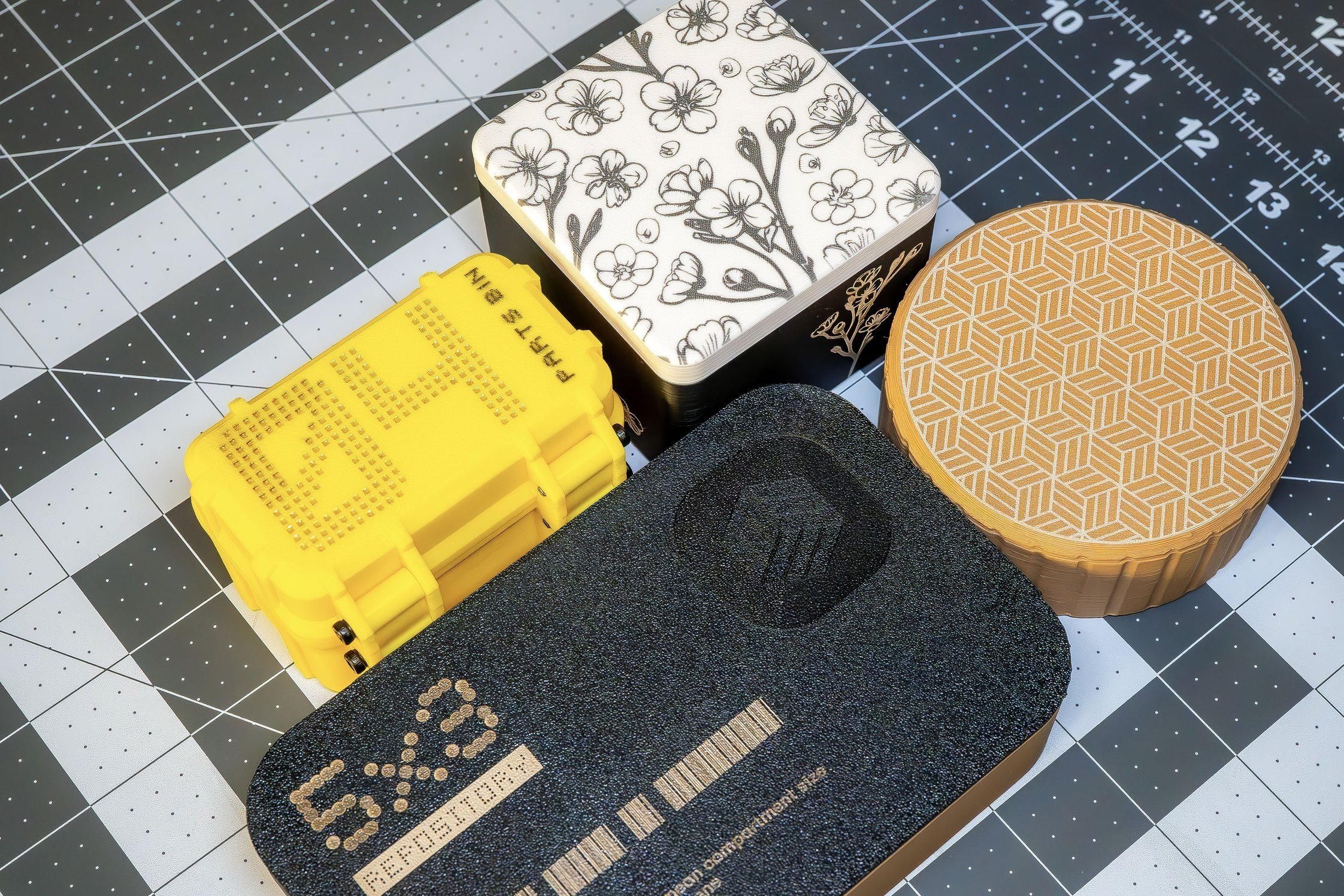
After assessing our findings, we designed and applied some graphics to some items we had available. Each graphic was designed specifically for each item taking into account the shape and dimensions of the surface to be applied to and the type of filament that item was printed with.
White ABS
2W IR laser; Engrave; Power 100; Speed 150; Pass 1; 260 lines per cm
Black ABS
2W IR laser; Engrave; Power 90; Speed 200; Pass 1; lines per cm 200
Yellow ABS
'04’ :
10W Blue Diode laser; Engrave; Power 100; Speed 200; Pass 1; lines per cm 240
2W IR laser; Score; Power 80; Pass 1
‘Parts Bin’ :
2W IR laser; Engrave; Power 100; Speed 200; Pass 1; lines per cm 240
Brown PLA
2W IR laser; Engrave; Power 100; Speed 200; Pass 4; lines per cm 240
Black ABS
2W IR laser; Engrave; Power 90; Speed 200; Pass 1; 200 lines per cm
2W IR laser; Score; Power 100; Speed 60; Pass 2
10W Blue Diode laser; Engrave; Power 90; Speed 600; Pass 1; lines per cm 200
10W Blue Diode laser; Score; Power 100; Speed 200; Pass 2
Conclusion
The first thing to point out is that the process of using a laser to apply marks or design to the surfaces of 3D printed objects is not straightforward. The outcomes can sometimes seem unpredictable and can often be surprising. For instance, a laser can produce a mark darker than the original material color for one type of filament, while the same laser at the same settings can produce a mark that is lighter for another filament; and yet for another filament, produce no discernible affect at all. In any case, the type of laser, the color of the filament, and the type of material the filament is all make a significant difference in the end result.
Though two general rules of thumb seem to be surfacing. One is that lighter colors tend to increase the likelihood that a laser will have a reduced or no effect. Another is that material that is the same or similar in color to the laser used on it will result in a reduced or no effect.
This is why we are recommending that anyone who intends to use laser engraving in the creation of their piece should take the step of printing a test plate for each filament to be used in the project. This plate can then be used to test what kind of effect the intended laser will have.
But once those baselines are established and expectations are grounded and/or confirmed, the potential for exceptional results can be quite high. Because the marks made in this process structurally change the material at a microscopic level (either by vaporizing, melting, and/or bubbling the filament) the design applied to 3D prints are extremely wear and weather resistant, and are at least as durable as the material itself. They will not wipe or chip off, and in many cases are more than just surface deep.
-
If you are interested in what we used for this process, you can find our materials below.
Hardware:
Bambu X1 Carbon
Bambu Textured Plate
xTool F1
Software:
Shapr3D Version 5.541.0.6373
Bambu Studio 1.8.4.51
xTool Creative Space
Materials:
White PLA
Grey PLA
Black PLA
Red PLA
Brown PLA
White ABS
Black ABS
Yellow ABS
Example 3D Prints
Fiiles we used as example pieces we etched on.
@waxounet - Square box (https://makerworld.com/en/models/149173#profileId-165899)
@ImaginationForg - Blank round box with screw top (https://makerworld.com/en/models/155442#profileId-170143)
@OlleMark - Screw & component box - small (https://makerworld.com/en/models/53524#profileId-55285)















































